06. 部署一个 Lambda 函数

通常,Lambda函数是“服务功能”。它允许您执行操作以响应某些事件,称为触发器Trigger。从本质上讲,您可以定义一个事件,当这些事件发生时,您的代码就会被执行。
例如,您可以设置一个触发器,以便每当将数据上载到特定的S3存储桶时,就会执行Lambda函数来处理该数据并将其插入到某个数据库中。
Lambda函数的一大优势是,由于Lambda函数中可包含的代码量相对较小,因此只需按执行次数收费。
在我们的例子中,我们创建的Lambda函数旨在处理用户输入并与我们部署的模型进行交互。此外,我们将使用的触发器是我们将使用API网关创建的终端。
- 设置Lambda函数
我们要做的第一件事是设置Lambda函数。只要我们的公共API发送了数据,就会执行此Lambda函数。执行时,它将接收数据,执行所需的任何类型的处理,将数据(审查)发送到我们创建的SageMaker端点,然后返回结果。
- 为Lambda函数创建IAM role
由于我们希望Lambda函数调用SageMaker端点,因此我们需要确保它具有执行此操作的权限。为此,我们将构建一个我们以后可以提供Lambda函数的 role。
* 使用AWS Console,导航到IAM页面并单击Roles。然后,单击“Create role”。
* 确保AWS服务是所选受信任实体的类型,并选择Lambda作为将使用此角色的服务,然后单击“Next: Permissions”。
* 在搜索框中键入Sagemaker,然后选中AmazonSageMakerFullAccess策略旁边的复选框。然后,单击“Next:Review”。
* 最后,命名Role。确保使用稍后会记住的名称,例如LambdaSageMakerRole。然后,单击“创建角色”。- 创建Lambda函数
现在是时候实际创建Lambda函数了。请记住,为了处理用户提供的输入并将其发送到我们的端点,我们需要收集两条信息:
- 终端的名称
- volcabulary
步骤:
- 首先,使用AWS控制台导航到AWS Lambda页面,然后单击“Create a Function"。
- 当您转到下一页时,请确保选择了"Author from Scratch"。
- 现在,命名你的Lambda函数并记住,例如sentiment_analysis_xgboost_func。确保选择了Python 3.6 runtime,然后选择您在上一部分中创建的role。然后,单击“Create Function”。
- 在下一页,您将看到有关您刚刚创建的Lambda函数的一些信息。如果向下滚动,您应该看到一个编辑器,您可以在其中编写将在您的Lambda函数被触发时执行的代码…您应该复制并黏贴下面的代码。
# We need to use the low-level library to interact with SageMaker since the SageMaker API
# is not available natively through Lambda.
import boto3
# And we need the regular expression library to do some of the data processing
import re
REPLACE_NO_SPACE = re.compile("(\.)|(\;)|(\:)|(\!)|(\')|(\?)|(\,)|(\")|(\()|(\))|(\[)|(\])")
REPLACE_WITH_SPACE = re.compile("(<br\s*/><br\s*/>)|(\-)|(\/)")
def review_to_words(review):
words = REPLACE_NO_SPACE.sub("", review.lower())
words = REPLACE_WITH_SPACE.sub(" ", words)
return words
def bow_encoding(words, vocabulary):
bow = [0] * len(vocabulary) # Start by setting the count for each word in the vocabulary to zero.
for word in words.split(): # For each word in the string
if word in vocabulary: # If the word is one that occurs in the vocabulary, increase its count.
bow[vocabulary[word]] += 1
return bow
def lambda_handler(event, context):
vocab = "*** ACTUAL VOCABULARY GOES HERE ***"
words = review_to_words(event['body'])
bow = bow_encoding(words, vocab)
# The SageMaker runtime is what allows us to invoke the endpoint that we've created.
runtime = boto3.Session().client('sagemaker-runtime')
# Now we use the SageMaker runtime to invoke our endpoint, sending the review we were given
response = runtime.invoke_endpoint(EndpointName = '***ENDPOINT NAME HERE***',# The name of the endpoint we created
ContentType = 'text/csv', # The data format that is expected
Body = ','.join([str(val) for val in bow]).encode('utf-8')) # The actual review
# The response is an HTTP response whose body contains the result of our inference
result = response['Body'].read().decode('utf-8')
# Round the result so that our web app only gets '1' or '0' as a response.
result = round(float(result))
return {
'statusCode' : 200,
'headers' : { 'Content-Type' : 'text/plain', 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' : '*' },
'body' : str(result)
}- 将上面的代码复制并粘贴到Lambda代码编辑器后,将** ENDPOINT NAME HERE **部分替换为我们之前部署的终端的名称。
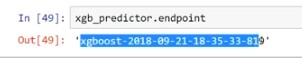
- 您还需要将volcabulary复制到 lambda_handler 方法开头的代码中的适当位置。
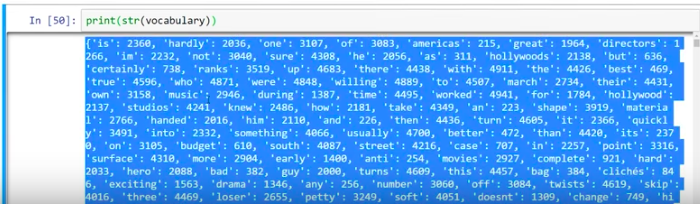
- 将端点名称添加到Lambda函数后,单击“保存”。您的Lambda功能现已启动并运行!